Methylene Blue Can Be Used to Stain Dna Because It
Home » Blog » Methylene Blue » What is Methylene Blue
Methylene Blue also known as Methylthioninium Chloride is an organic chlroride salt that appears as a bright greenish colourful compound and is commonly used to treat pediatric and adult patients with aquired methemoglobinemia. Methylene blue belongs to the class of compounds known as "Phenothiazine's" and more particularly "Diamino Phenothiazine's". Methylene Blue is also on the list of World Health Organization's list of essential medicines.
A German Chemist named Heinrich Caro first prepared Methylene Blue in the year 1876. It was originally synthesized as an aniline based dye for the textile industry, but scientists such as Robert Koch and Paul Ehrlich realized that it also has potential for use in microscopy stains. Methylene Blue was also used for treating malaria in Africa but this treatment disappeared after chloroquine and other drugs entered the market. This compound was also previously used to treat urinary tract infections and cyanide poisoning. Methylene Blue is also under clinical trial phase for its potential effectiveness in treating patients with Alzheimer's disease.As a dye methylene blue is used as a staining agent for performing surgeries, in diagnostics and also for microscopy.

Note for the reader – In a few instances, this article refers to Methylene Blue as MB.
Methylene blue is an electron carrier and is reduced to Leuco Methylene blue by the enzymes NADPH reductase which allows it to function against malaria and methemoglobinemia. It's also beneficial in cytotoxic circumstances in the brain since it promotes cellular oxygen intake while reducing anaerobic glycolysis. It is known to generate singlet oxygen upon exposure to light because of which it is also known to be one of the best Photosensitizer, Photodynamic agents for use in the treatment of cancer and antibiotic-resistant infections.

Macsen supplies cGMP manufactured methylene blue API for various research applications like virology, oncology, photodynamic, photodynamic therapies, oxidative stress-related diseases and therapies, anti-ageing, rheumatology, urology, Alzheimer which is the most common cause of dementia.
Chemistry of Methylene Blue
Structure of Methylene Blue
Methylene blue is a complex organic compound that has three cyclic structures attached in a chain. Sulphur and nitrogen are attached to the central ring, and chlorine is in a separate group and is negatively charged.

| PROPERTIES OF METHYLENE BLUE | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC Name | [7-(dimethylamino)phenothiazin-3-ylidene]-dimethylazanium;chloride |
| Product Name | Methylene Blue/ Methylthioninium Chloride |
| Synonyms | Methylthioninium Chloride ; Basic Blue 9 ; Zinc free Methylene Blue ; C.I 52015 ; Methylene Blue Trihydrate; Swiss Blue |
| CAS No | 122965-43-9 |
| Molecular Formula | C16H18ClN3S |
| Molecular volume | 390.2 (cm3/g mol) |
| Melting Point | 100 to 110 °C (with decomposition) |
| Colour/Form | Dark green crystals or powder |
| Colour of Solution | Deep blue colour |
| Odour | Slight odour |
| Solubility | Slightly Soluble in Water and in Alcohol |
| Storage Condition | Keep container tightly closed, in a cool, well-ventilated place. |
| Stability/Shelf Life | Stable under recommended storage conditions |
| Decomposition | When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes |
| CAS No (Others) | 61-73-4 (anhydrous), 7220-79-3 (Trihydrate) |
| UNique Ingredient Identifier (UNII) code | 8NAP7826UB |
| Wavelength | 664 nm |
| Absorbance | Maximum at 668 nm in visible light region |
Other Chemical Properties
- Methylene Blue becomes acidic when dissolved in water
- It forms a deep blue solution when dissolved in water or alcohol
- It is soluble in ethanol, chloroform, slightly soluble in pyridine; insoluble in ethyl ether
- When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides and chloride
Reference: Methylene Blue Chemical & Physical Properties
Preparation of Methylene Blue
Methylene blue is a derivative of Phenothiazine. The compound is prepared or synthesized by oxidation of oxidation of dimethyl-4-phenylenediamine in the presence of sodium thiosulfate.
Uses of methylene blue dye
Methylene Blue is a US FDA approved treatment for aquired methemoglobinemia. It acts as an antidote for cyanide and ifosfamide poisoning. It is also being researched for its antimalarial and anti-Alzheimer's efficacy. Apart from the medical applications for humans methylene blue is also a popular anti-fungal and anti-parasitic treatment in aquaculture.
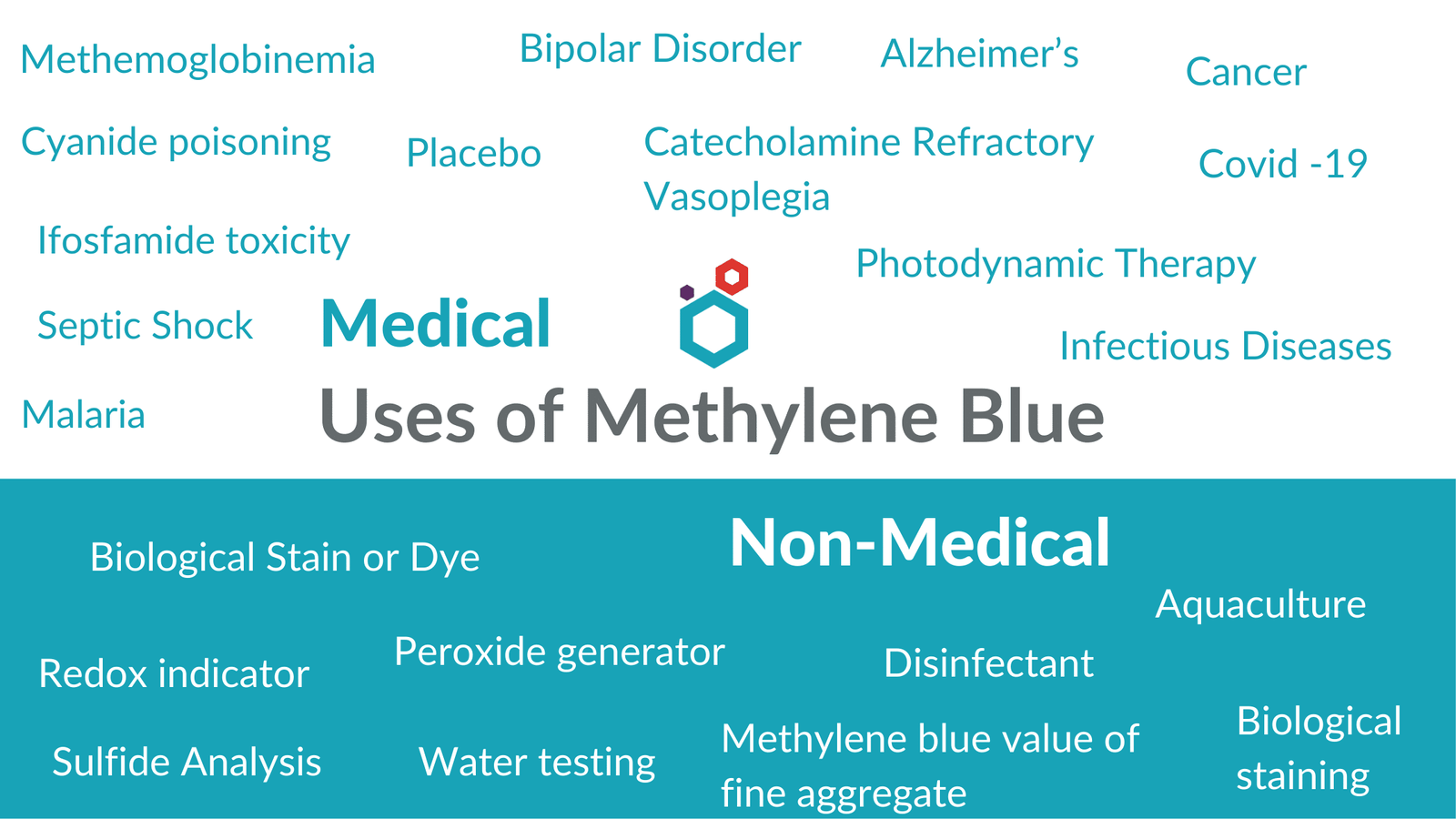
To discuss the uses of methylene blue in detail we can classify them into two categories – Medical & Non-Medical.
Medical Uses of Methylene Blue
Methemoglobinemia
Methemoglobinemia occurs when there is an excess of methemoglobin in the blood. Methemoglobinemia can develop as a result of exposure to certain medications or toxic substances, such as nitrites. Methemoglobin is also a type of haemoglobin but it doesn't help in carrying oxygen as haemoglobin does. It's found in the blood in little quantities. But, if the level of methemoglobin rises, it becomes difficult for blood to circulate oxygen. It results in oxygen deficit throughout the body and causes symptoms like blue or pale skin.
Methemoglobinemia is treated with methylene blue injection. Treating methemoglobinemia is currently the main use of Methylene Blue in medicine which is also approved by the US FDA. When given intravenously as an antidote, methylene blue is first converted to leucomethylene blue, which subsequently converts the heme group from methemoglobin to haemoglobin. Methylene blue can shorten methemoglobin's half-life literally from hours to minutes. Methylene blue converts methemoglobin to a more effective type of haemoglobin that transports oxygen more efficiently throughout the body. It oxidizes NADPH in the methemoglobin formation pathway and is thus useful in the prevention of this disease.
Cyanide poisoning
For more than a century, physiologists have employed cyanide as a substitute for anoxia in a variety of experimental situations, anticipating that inhibiting the metalloenzymes that are present in mitochondrial complexes by CN would replicate the acute consequences of a decrease in O2 supply.
Cyanide poisoning happens due to various reasons such as industrial exposure, smoke inhalation, or bioterrorism causes cardiogenic shock and necessitates an immediate antidote. Methylene blue reduces cyanide toxicity by restoring oxidation-reduction equilibrium and Ca2+ channel function.But this use is no longer recommended.
Research reference –Methylene Blue as an Antidote for Cyanide and Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Placebo
A placebo is a medication or therapy that is intended to have no therapeutic value but can influence how patients perceive their illness and promote the body's chemical processes for pain relief and other symptoms while having no effect on the disease itself.
Methylene blue is used as a placebo by physicians. They would advise their patients to anticipate their urine to change colour as an indication that their illness has improved.
Research reference – The Ethics of Deception in Medicine
Ifosfamide toxicity
Methylene blue is used to treat ifosfamide neurotoxicity.
Ifosfamide's toxic metabolite affects the mitochondrial respiratory chain, resulting in NADH buildup. Methylene blue functions as an alternative electron acceptor to reverse NADH suppression of hepatic gluconeogenesis prevents the transition of chloroethylamine into chloroacetaldehyde, and inhibits numerous amine oxidase activities, preventing the production of CAA.
Methylene blue dosage for the treatment of ifosfamide neurotoxicity differs depending on whether it is used concurrently as an adjuvant in ifosfamide infusion or to reverse mental symptoms that emerge after the conclusion of an ifosfamide infusion.
Research reference – Ifosfamide neuropsychiatric toxicity in patients with cancer, Methylene blue for management of ifosfamide induced encephalopathy
Septic Shock
Septic shock is a potentially deadly medical condition that takes place when organs are injured or damaged due to infection, resulting in dangerously low blood pressure and cellular metabolic problems. In severe conditions, it can cause multiple organ failures.
Methylene blue has been effective in treating this condition. Methylene blue has mostly been used in adults, although it is also said to be effective in children. It works by inhibiting the nitric oxide-cyclic guanosine monophosphate pathway, which is active during a septic shock. Methylene blue is effective in instances where conventional medicines have failed.
Research reference – Methylene blue for a distributive shock: potential new use of an old antidote
Other Medical Uses of Methylene Blue as Upheld by Research
Catecholamine Refractory Vasoplegia
Vasoplegia is a common consequence following cardiopulmonary bypass. In such circumstances, methylene blue may be an appealing therapeutic option.
Methylene blue appears to be an effective treatment for norepinephrine-refractory vasoplegia following cardiopulmonary bypass in the majority of patients, with no apparent adverse effects.
Research reference – Methylene Blue: Magic Bullet for Vasoplegia
Alzheimer's
The primary cytopathologist in Alzheimer's disease patients' brains is mitochondrial failure and energy hypometabolism, which are most likely caused by the buildup of harmful amyloid-beta peptides.
The use of Methylene Blue helps to avoid mitochondrial malfunction and to reduce energy hypometabolism. Methylene blue improves heme production, cytochrome c oxidase, and mitochondrial respiration, all of which are compromised in patients' brains. Methylene blue has consistently proven to be one of the most effective drugs for delaying senescence in normal human cells.
But, the drug LMTM a derivative of methylene blue failed in phase 3 of clinical trials for Alzheimer's, as reported by the company undertaking the research, TauRx Pharmaceuticals. The drug failed to show a cognitive decline in mild to moderate Alzheimer's patients.
Research reference – In First Phase 3 Trial, the Tau Drug LMTM Did Not Work
Malaria
Methylene blue's initial medicinal application was as a malaria therapy.
Methylene blue has shown exceptional antimalarial efficacy in cell culture studies. Animal studies have shown that resistance to methylene blue is quite low and that's why it is used as an antimalarial agent.
Research reference – Strong Gametocytocidal Effect of Methylene Blue-Based Combination Therapy against Falciparum Malaria: A Randomised Controlled Trial, Methylene blue for malaria in Africa: results from a dose-finding study in combination with chloroquine
Bipolar Disorder
In people with bipolar illness, residual symptoms and cognitive impairment are significant sources of disability. Because of its possible neuroprotective properties, methylene blue as an adjunctive medication helps reduce such symptoms.
Research reference – In First Phase 3 Trial, the Tau Drug LMTM Did Not Work
Cancer
Methylene blue staining is an important diagnostic tool in a major community-based oral cancer screening programme for high-risk patients.
MB-PDT (methylene blue- photodynamic therapy) has the potential to be a highly efficient technique that can be used as a powerful adjunctive treatment for surgery of breast tumours, and possibly other types of tumours, to safely increase the elimination rate of microscopic residual disease, reducing the risk of both local and metastatic occurrences.
Research reference – Methylene blue photodynamic therapy induces selective and massive cell death in human breast cancer cells, Photodynamic therapy using methylene blue in lung cancer animal models
Photodynamic Therapy
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is an advanced treatment for cancer and other health ailments. The activation of a photosensitizer in the presence of oxygen by a certain wavelength of light increases cellular damage in PDT. Methylene blue is useful in PDT because of its ability to produce singlet oxygen and its established photodynamic activity in therapeutic applications against many tumours and diseases.
Research reference – Photodynamic therapy using methylene blue to treat cutaneous leishmaniasis, Methylene blue-mediated photodynamic therapy enhances apoptosis in lung cancer cells
Infectious Diseases
Methylene blue is a dye that binds to biological components. When it is exposed to light, the dye becomes active and causes damage to the wall to which it is bound. This technique has been widely utilized to turn viruses inactive hence, preventing a lot of infectious viral diseases.
Research reference – Nonphotodynamic Roles of Methylene Blue: Display of Distinct Antimycobacterial and Anticandidal Mode of Actions, Methylene blue photochemical treatment as a reliable SARS-CoV-2 plasma virus inactivation method for blood safety and convalescent plasma therapy for COVID-19
Covid -19 (Corona Virus Disease)
As a low-cost, widely available drug, Methylene Blue has a significant potential role in the treatment of COVID19.
According to doctors, methylene blue is a century-old blood pressure enhancer and is usually prescribed when a patient's oxygen saturation level drops.
Non-Medical Uses of Methylene Blue
Biological Stain or Dye
Methylene blue is a dye that was originally created to stain and inactivate certain microorganisms. It is used in staining preparations in histology today.
In contrast to many other phenothiazine medicines, methylene blue possesses an oxidized phenothiazine ring structure. This difference has a significant impact on action and activity because it raises the angle of the chemical structure and provides the ring system with a positive charge. This can help with intracellular dispersion, allowing methylene blue chemicals to flow within blood cells.
Examples are; Staining with Methylene blue reveals membrane degradation. It's also used to stain blood samples. It distinguishes between immature and adult blood cells and is used to demonstrate erythropoiesis (red blood cell formation) and age-related degradation.
Redox indicator
Methylene blue is an excellent redox indicator.
Methylene blue shows the presence or absence of oxygen through colour. When there is oxygen present, water containing the methylene blue indicator becomes blue. By sealing a solution of water and methylene blue and violently shaking it to mix oxygen into water, a deep blue colouration is obtained. The blue hue fades when oxygen is eliminated from the solution.
Peroxide generator
Methylene blue is a photosensitizer that, when exposed to oxygen and light at the same time, produces singlet oxygen. It is utilized in this context to produce organic peroxides via a Diels-Alder reaction, which is spin prohibited with ordinary air triplet oxygen.
Sulfide Analysis
This sulphide analysis is based on the capability of H2S and acid-soluble metallic sulphides to directly convert N, N Dimethyl-p-phenylenediamine to methylene blue in the presence of an oxidising agent.
The intensity of the methylene blue colour development is related to the quantity of sulphide in the initial sample taken This method is also known as the methylene blue technique.
Water testing
Methylene blue is an indirect indication of dissolved oxygen content. When there is oxygen present, the indicator becomes blue. In a reducing environment, however, it transforms into a colourless leuco-compound. As a result, it may be used to determine whether or not there are oxygen-consuming chemicals in the water sample.
It's used in water testing such as BOD.
Methylene blue value of fine aggregate
The number and properties of clay minerals present in the test sample influence the methylene blue value. The small granular structure and surface activity of Clay minerals raise the quantity of water required for mixing to achieve workability in concrete. Though the amount of microfine material in fine aggregate is limited, the methylene blue value rises when clay-derived components are present.
Disinfectant
Methylene Blue works as a disinfectant owing to its antibacterial and antiparasitic activity on bacteria and other parasites, which is most likely due to its interaction with cytoplasmic structures within the cell as well as its involvement with redox processes.
Biological staining
Methylene Blue is a positively charged stain ( blue dye) that binds to negatively charged components of cells such as the nucleus (DNA) and RNA in the cytoplasm. Methylene blue is a popular stain that allows us to view tiny life in vivid colour. It may also be used to assess whether eukaryotic cells like yeast are alive or dead.
Aquaculture
Methylene blue's function in aquaculture is that it acts as an anti-fungal and anti-parasitic, and it is widely used to treat fish eggs to prevent fungal overgrowth. Methylene Blue is often a safe aquarium disinfectant that could also be used to cure ammonia and nitrite toxicity.
Side Effects Of Methylene Blue
The common side effects of methylene blue include bluish-green colouration of urine and stool, nausea, vomiting, skin discolouration, headache, dizziness and diarrhoea.

Methylene Blue Injection Side Effects
Methylene blue injection side effects sometimes require immediate medical attention and sometimes it doesn't. Here is the list of some side effects of methylene blue.
Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
There are a few side effects of methylene blue that an overdose of the medication might have caused and that require immediate medical attention. The side effects include:-
- Bluish-coloured lips
- Fingernails, or palms agitation
- Coughing
- Fits
- Black urine
- Dizziness or light-headedness
- Fever with rapid heartbeat
- Severe headache
- Massive hive-like swelling on the face, eyelids, lips, tongue, neck, hands, legs, feet
- Reflexes that are hyperactive, poor coordination in working
- Fastened heartbeat
- Shivering
- Sore throat
- Extreme sweating
Refer here for more details.
Not requiring immediate medical attention
Sometimes methylene blue side effects may occur, although they typically do not necessitate medical care. These adverse effects may subside as the body responds to the medication. In addition, the health care provider will be able to advise you on how to avoid or mitigate some of these adverse effects. Consult the doctor if any of the following side effects persist or become bothersome, or if you have any concerns about them.
More common side effects
- Changes in taste
- Skin colour
- Feeling warm or chilly
- Increased perspiration
- Loss of flavour
- Muscle or joint discomfort
- Pain where the injection is given
- Soreness in the arms and legs are all possible side effects.
Less common side effects
- Back pain
- Rashes
- Shivering
- A general sense of discomfort or sickness
- Blue or purple spots on the skin
- Reduced appetite
- Muscle aches
- Muscle spasms
- Runny nose
- Sleep disturbances.
Methylene Blue Oral Side Effects
Methylene Blue as an oral medicine is used as a diagnostic tool to detect the presence of a gastrointestinal fistula (e.g., gastrointestinal fistula diagnosis). A modest amount (e.g., 5—10 ml) of methylene blue is given orally or via a nasogastric tube to adult patients with a suspected gastrointestinal fistula. The blue colouring of ascitic or peritoneal fluid indicates the presence of a communicating fistula with the gastrointestinal system. The side effects associated with the oral administration of methylene blue are categorized as follows:
Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
- Irritation in the urinary bladder and difficulty in urinating
- Persistent fever
- Constant fatigue
- Dizziness
Not requiring immediate medical attention
- Bluish-green urine and stool colouration
- Severe diarrhoea
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Skin discolouration
Refer here for more details.
Methylene Blue Side Effects on Skin
In skincare, the application of antioxidants is an effective approach to delay the process of skin ageing. Researchers have found evidence that the antioxidant property of Methylene Blue can be used to slow down and reverse the signs of ageing. Fibroblasts treated with methylene blue have displayed increased cellular lifespan, improved cell proliferation and reduced expression of P16 (a biomarker of ageing). Based on the findings of the study, methylene blue can be effectively used to protect the skin from oxidative stress and delay skin ageing. Associated side effects include:
• Staining of skin
• Injection site necrosis (SC)
Important precautions one should be aware of before taking Methylene Blue
- Methylene Blue (methylene blue injection) should be administered intravenously very slowly to avoid the chemical's local high concentration from generating more methemoglobin. Its dosage should not be increased without the doctor's recommendation.
- It takes up to 30 minutes to complete the IV infusion. While getting methylene blue, there are a few things that should be in check such as respiration, blood pressure, oxygen levels, renal function, and other vital indicators that should be continuously monitored.
- Methylene blue is most likely responsible for the patient's urine or stool becoming blue or green. This is a common side effect of methylene blue and has no harmful consequences. This impact, however, may show unexpected results with some urine tests.
- Methylene blue is not recommended for individuals who have had hypersensitive responses to it, as well as those who have significant renal insufficiency. It is generally contraindicated in G6PD deficient patients due to the risk of acute hemolysis, as well as in patients with Heinz body anaemia.
- It should not be used with an SSRI or serotonin-boosting medication.
- Babies are especially susceptible to the harmful effects of methylene blue. Hyperbilirubinemia, increased meth-haemoglobin production, pulmonary oedema, hemolytic anaemia, respiratory disorder, and phototoxicity are among the common side effects.
- MB also interacts with the light emission of the pulse oximeter, leading to an incorrectly low oxygen saturation measurement.
- It may also induce an increase in blood pressure. It inhibits nitric oxide (NO) activities, which raises blood pressure and myocardial function in septic shock. It raises mean arterial blood pressure in humans with septic shock via increasing cardiac index and systemic vascular resistance.
- Methylene blue might induce impaired vision and interfere with your thoughts or reflexes. Avoid exposure to sunlight for at least 24 hours following methylene blue therapy. This medication might make you more susceptible to sunburn. When going out, make sure to wear protective clothing and apply good sunscreen.
- The patient should talk to the doctor if they are allergic to methylene blue or if they have any other allergies prior to taking it. If they have specific medical problems, then they should not use this medicine.
- Doctors should be informed about the patient's medical history, particularly if they have renal issues, before using this medicine.
- This medicine should be taken only when absolutely necessary during pregnancy. Consulting the doctor about the dangers and benefits is absolutely necessary. Pregnant and lactating women should be careful with taking the medicine and only take it if necessary and be advised by the doctor.
FAQs
Is methylene blue FDA approved?
The intravenous form of methylene blue is approved by the FDA for the treatment of pediatric and adult patients with acquired methemoglobinemia.
Can methylene blue be given orally?
To treat methemoglobinemia and urinary tract infections, methylene blue injection can either be taken orally or injected intravenously. Both administration methods are effective.
What is recommended if a person swallows methylene blue?
Rinse mouth thoroughly with water. Do not induce vomiting unless under the direction of medical personnel. If in doubt, get medical attention promptly.
Is methylene blue anti-inflammatory?
Growing research has shown that MB restores aberrant vasodilation and, importantly, it may even be involved in pain alleviation. By inhibiting the formation of nitric oxide, MB reduces inflammation and, ultimately, alleviates pain.
Is methylene blue carcinogenic?
Methylene Blue has the potential to be carcinogenic.
What is methylene blue made of?
Methylene blue is a thiazine dye. Chemically, it is an organic chloride salt having 3,7-bis(dimethylamino)phenothiazin-5-ium as the counterion.
What family of dyes does methylene blue belong to?
Methylene blue belongs to the phenothiazine family.
Is methylene blue acidic or basic?
Methylene blue is a thiazine dye that is basic in nature.
Does Methylene blue dissolve in water?
Methylene blue is a cationic dye that dissolves in water and organic solvents to give blue-coloured solutions.
Is methylene blue a pH indicator?
Methylene blue (0.1%) in combination with methyl red (0.03%) in ethanol or in methanol acts as Tashiro's indicator which is a pH indicator for pH value: 4.4–6.2.
Why is methylene blue used in surgery?
Methylene blue (1%) has been used IV for over 30 min in ICU 1 hour before surgery. Methylene blue (MB) is occasionally applied extravascularly during a variety of vascular procedures to assist in the orientation of the blood vessel. The use of marking dyes serves to facilitate isolation and may therefore reduce surgical trauma.
Can you pour methylene blue down the sink?
It might be okay to treat the methylene blue with bleach and put it down the drain, however, It really depends on how concentrated it is.
What happens when methylene blue is added to milk?
Methylene blue solution forms blue colour in the milk when added, although it loses its colour as the level of oxygen gets depleted in the milk.
Is methylene blue hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
Methylene Blue is a hydrophobic molecule.
Is methylene blue antifungal?
Methylene blue exhibits antifungal properties through mitochondrial dysfunction and disruption of redox and membrane homeostasis against C. albicans.
Where to buy Methylene blue?
MB dye is commonly available at laboratory chemical stores, but MB procured through such means is meant for laboratory application only and is unsuitable for human or veterinary use due to the presence of several organic and inorganic impurities such as carcinogens, heavy metals, and other contaminants.
Methylene Blue for medical use is currently available as MB (1% – 0.5%) injections which are made using USP or Ph. Eur grade MB API. Only a few companies provide USP or Ph. Eur quality methylene blue API under cGMP (current good manufacturing procedures) conditions with legitimate FDA authorisation.
Macsen Drugs, a unit of Macsen Labs, is one of the leading cGMP manufacturers of MB API with WHO-GMP Certification, USFDA and USDMF registration.
How pharma grade of methylene blue is different from ordinary methylene blue dye?
MB is a very commonly made and used dye for various dying applications like textile, paper etc. the process of manufacturing dye grade MB uses highly toxic chemicals and toxic heavy metals.
The dye grade MB need not be purified further for the removal of organic and inorganic impurities. Pharmaceutical grade MB is manufactured using a process that uses high-quality raw material which is quite less toxic and the use of metal-based chemicals is minimized or avoided and a lot of purification process is involved in manufacturing like- Re-crystallization, filtration, chromatographic purification, ION- exchange etc, which renders the MB free from organic and Inorganic impurities making it suitable for various pharmaceutical applications.
Pharma grade MB typically contains less than 5% Azure B, and less than 01% of any other organic impurities like Azure C, Azure A, thionin, MVB, DMA etc. It has fewer than 1 ppm of very harmful metals like mercury and cadmium and less than 10 ppm of less dangerous metals.
Pharma grade MB must conform to all the specifications of the MB monograph of either USP or Ph. Eur Latest versions.
Can I use lab-grade methylene blue for pharma application?
It is not at all advisable to use the cheap lab grade of MB for any human or veterinary pharma application and such use can cause serious and life-threatening toxicity.
Can I use Methylene blue to confirm old pharmacopoeia monographs like USP-39/38, BP-73, BP-2000 etc for pharma application?
The old pharmacopoeia grades of MB are presently used for laboratory and diagnostic applications in pathology labs but they are not suitable for any human or veterinary pharmaceutical application. Only the latest USP or Ph. Eur monograph quality should be used for pharma applications.
Is Methylene Blue Zinc Salt the same as pharmaceutical grade methylene blue?
No, the zinc salt of Methylene blue is different from pharmaceutical grade MB which is not suitable for pharma application. The pharmaceutical MB is a zinc free form and only chloride salt form of MB.
Where to buy pharmaceutical grade Methylene Blue?
You can buy pharmaceutical grade methylene blue from an API manufacturer who holds necessary licenses for manufacturing USP, BP, or EP grade MB. It is also important to make sure that the organization manufactures the MB in a GMP environment.
Why does methylene blue turn colourless?
Methylene Blue is widely used as a redox indicator. It turns colourless when exposed to a reducing agent but again turns blue when oxidized.
Does methylene blue expire?
Methylene blue can expire in a few months because it is sensitive to higher temperatures above 30 º . It shows fast degradation at 40 º. It degrades by demethylating into various compounds like Azure A, Azure B, Azure C. Methylene blue is sensitive to light so exposure to strong light or UV rays, it gets degrades. If it is stored in cold storage then it can stay for 2-3 years.
How long does it take for methylene blue to work?
According to some studies, taking up to six doses each day can boost effects in as little as 10 minutes or as long as several days.
What is methylene blue used for?
We use methylene blue to treat methemoglobinemia and urinary tract infections. We use methylene blue as a dye or staining agent during surgery and other diagnostic exams to make it easier to see tissues and some body fluids.
What is methylene blue used for in biology and microbiology?
Methylene Blue staining is useful in determining cell mortality. It's also employed as a pigment in microbiology to analyze nucleic acid chains. It can be added to a solution to colour RNA and DNA for visual analysis.Refer here to know more.
Does methylene blue cause high blood pressure?
According to research studies conducted on human septic shock, methylene blue increases mean arterial blood pressure through an increase in cardiac index and systemic vascular resistance.
Is methyl blue the same as methylene blue?
No, both are different chemical compounds in structure, function and uses. Refer here for more details.
Is methylene blue harmful to humans?
Methylene blue is safe to use, provided it is taken as per the doctor's advice in a regulated amount. It certainly turns the urine or stool blue or green in appearance. This is a common side effect of taking methylene blue and will have no major harmful consequences. This impact, however, may result in unusual findings with some urine tests.
How often can I use methylene blue?
It is usually taken 3 times a day or as directed by the doctor, depending on the seriousness of the ailment. It should not be taken more than what is prescribed by the doctor as overdose can cause severe side effects.
Is methylene blue harmful to the skin?
Methylene blue can stain the skin blue, and it is difficult to remove the stain. While taking methylene blue medication, mild skin discolouration is observed.
Who should not take methylene blue?
If you are a mother who is producing milk and nursing or you have glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency then you should not be treated with methylene blue. Also, In a diabetic patient, methylene blue therapy lowers body weight while increasing blood glucose levels and glycated haemoglobin concentrations.
Read our other articles here
- Methylene Blue Against Cyanide Poisoning
- Methylene Blue & Covid-19
- Methylene Blue Injection: Indications, Dosage & Brands
- Methylene Blue in the treatment of Alzheimer's
- Malaria Treatment with Methylene Blue
Disclaimer-
The information provided here is based on general knowledge, articles, research publications etc and we do not claim the authenticity of any of the information provided above. We do not claim or suggest/advise any medical, therapeutic, health or nutritional benefits of MB. We do not supply or promote our MB product for the applications which are covered by valid patents and which are not approved by the FDA.
Macsen Labs is a manufacturer and supplier of several grades of Methylene Blue compound such as:-
- Methylene Blue USP
- Methylene Blue Zinc Free
- Methylene Blue BP 2000
- Methylene Blue BP 1973
- Methylthioninium Chloride BP
- Methylthioninium Chloride EP 9.0
- Methylthioninium Chloride E.P-10
Macsen Labs group's Methylene Blue Synthesis Process was granted a patent from the Indian patent office
The Indian Patent Office granted a patent to Mr Achal Agrawal, CEO of Macsen Labs, Udaipur. The title of the patent is Novel Improved Method for Synthesis of Diaminophenothiazine Compounds and it concerns a novel process for synthesising the compound Methylthioninium Chloride or Methylene Blue. Macsen Labs has now achieved a unique position by this patent and from now nobody will be able to copy this process. Read more

schneiderolve1987.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.macsenlab.com/blog/methylene-blue-chemistry-uses-side-effects/

0 Response to "Methylene Blue Can Be Used to Stain Dna Because It"
Post a Comment